Self-test for the detection of occult blood in the feces


The acronym FOB (Fecal Occult Blood) indicates the presence of occult blood in the stool, due to various gastrointestinal disorders such as: polyps, ulcers, colitis, diverticula, rhagades, hemorrhoids or tumor.
read moreThe symptoms of these lesions are often silent in the early stages, for this reason the search for occult blood in the feces represents an important screening test that allows to early identify the presence of pathologies affecting the gastrointestinal system.
BOWEL-FOB TEST is useful for identifying the presence of blood in the stool, in some cases not identifiable with the naked eye, especially over 45 years of age.
read moreIn some cases, the presence of occult blood in the stool is not clearly visible to the naked eye, so it is useful to use devices capable of doing so, without food restrictions before its use.
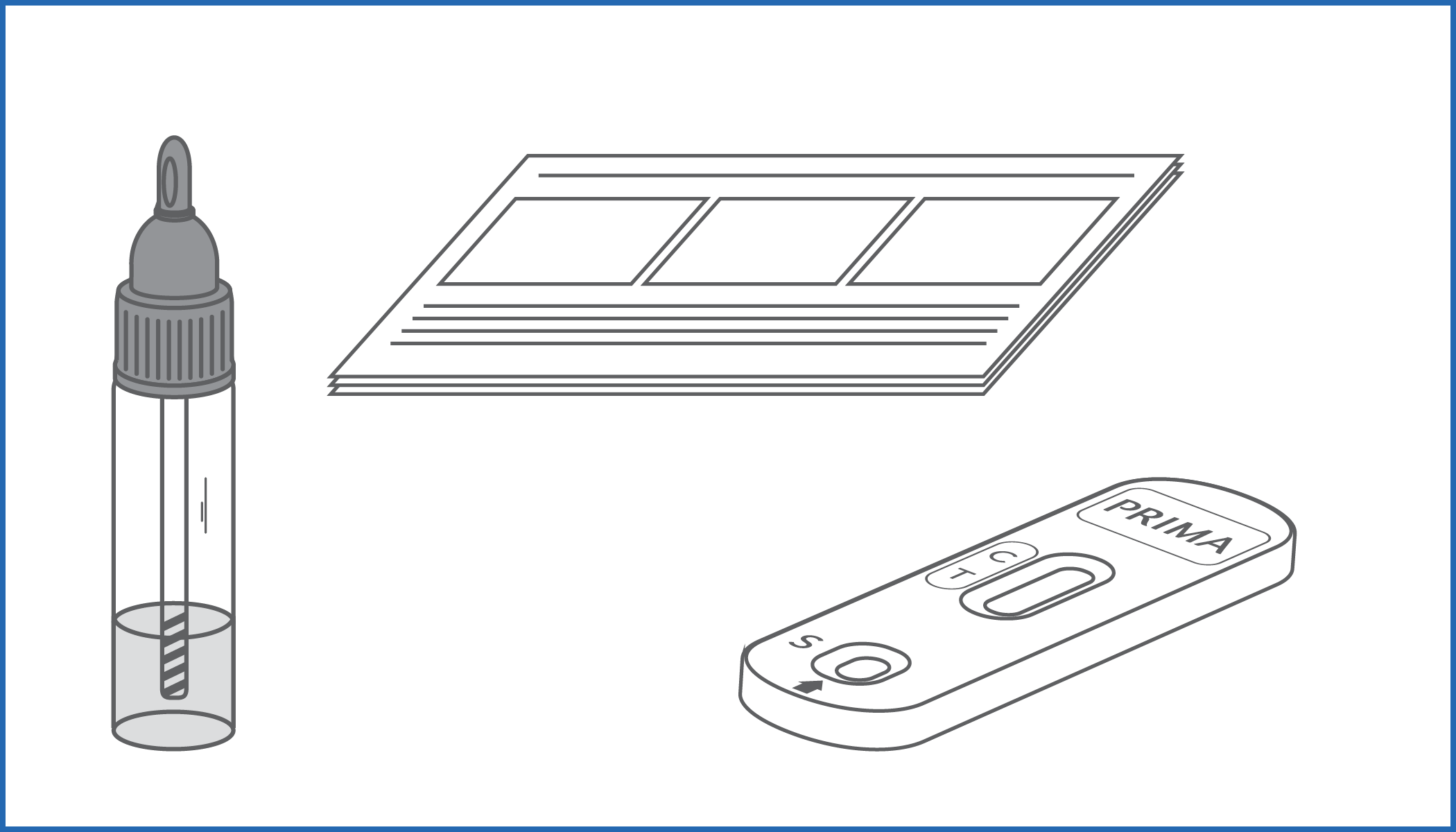
BOWEL-FOB TEST is an immunochromatographic device that detects the smallest amounts (above 40 ng/mL) of occult blood in stool samples.
| Specificity | 99% |
| Sensitivity | 78.7% |
| Accuracy | 92.6% |



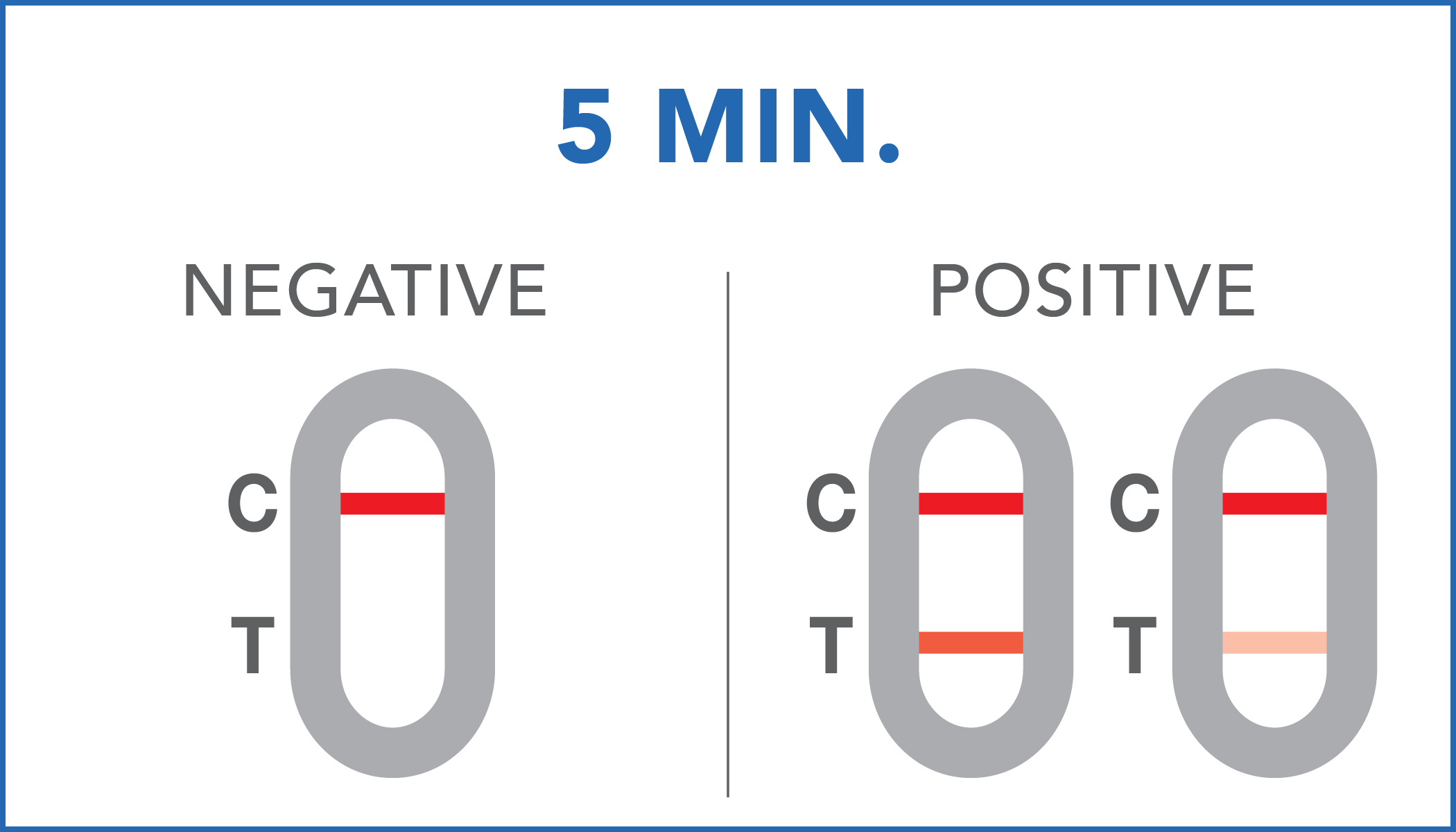
| Negative | the presence of occult blood in the feces has not been detected or its concentration is below the reference cut-off. |
| Positive | the presence of occult blood in the feces has been identified. Positive results can also be obtained in the presence of hemoglobin concentrations between 40 ng/mL and 36 ng/mL. It is recommendable to further check with your doctor. |
1. Van Rossum Leo G. et al.: “Random Comparison of Guaiac and Immunochemical Fecal Occult Blood Tests for colorectal Cancer in a Screening Population” Gastroenterology, Volume 135, Issue 1, 82 – 90.
2. Faivre J., Dancourt V., Denis B., Dorval E., Piette C., Perrin P., Bidan J.M., Jard C., Jung S., Levillain R., Viguier J., Bretagne J.F.: “Comparison between a guaiac and three immunochemical faecal occult blood tests in screening for colorectal cancer”. European Journal of Cancer. 2012; 48(16):2969-76.
3. Benton S.C., Seaman H.E., Halloran S.P.: “Faecal Occult Blood Testing for colorectal Cancer Screening: the past or the Future”. Current Gastroenterology Reports. 2015; 17(2):428
4. European Commission. European guidelines for quality assurance in colorectal cancer screening and diagnosis. First edition 2010
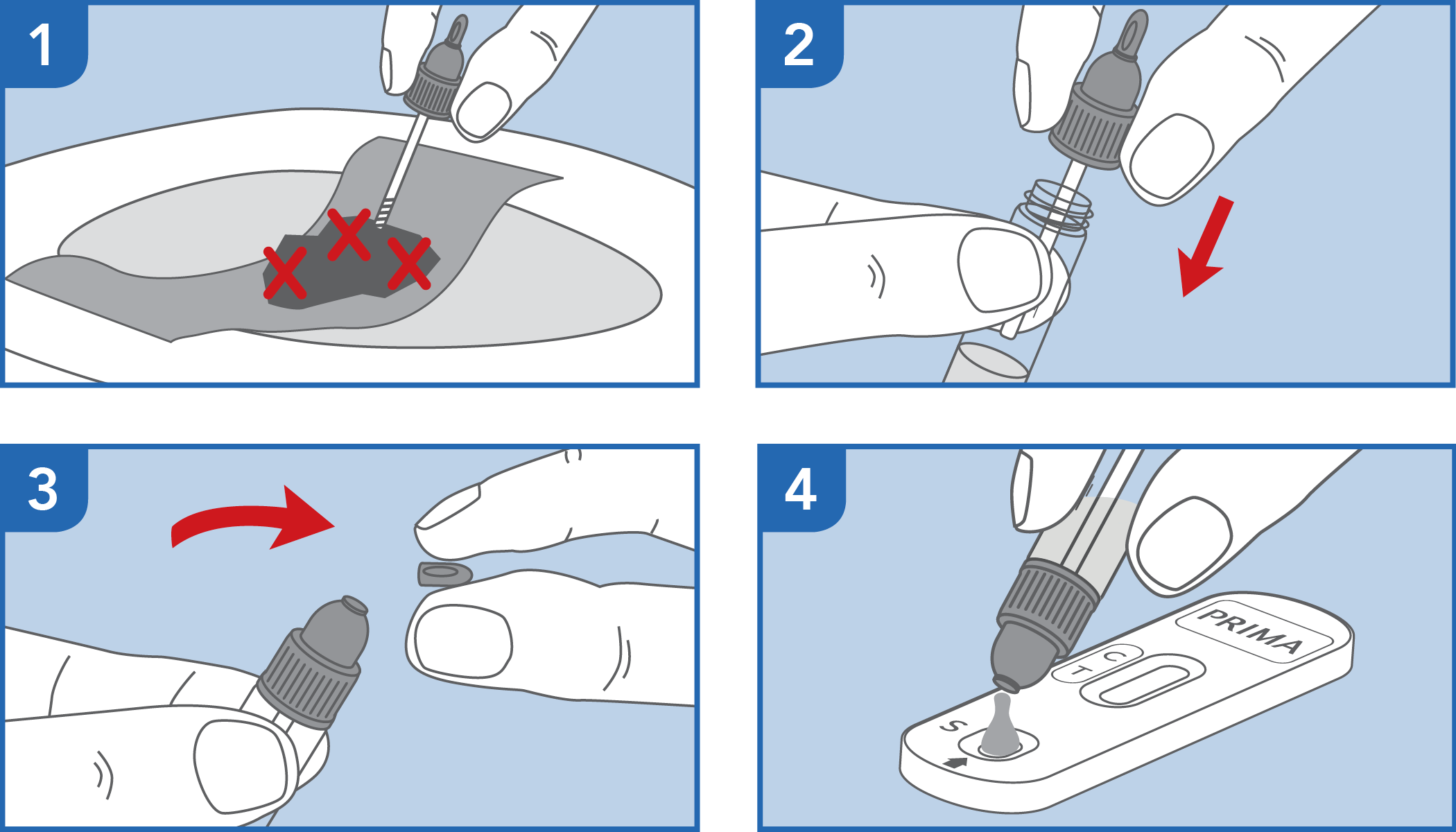
The test has been carried out correctly when the instructions for use are followed. It includes the reading time and the interpretation of the results shown at the "RESULTS INTERPRETATION" section of the instructions for use.
A colored line will appear at the control region (C) on the test device, showing that the test performed correctly. The absence of the colored line suggests to repeat the test with a new device and a new sample.
The color and intensity of the lines do not affect the interpretation of the result. The test has to be considered positive regardless of the color intensity of the test line (T).
Check product availability with the local representative in your country