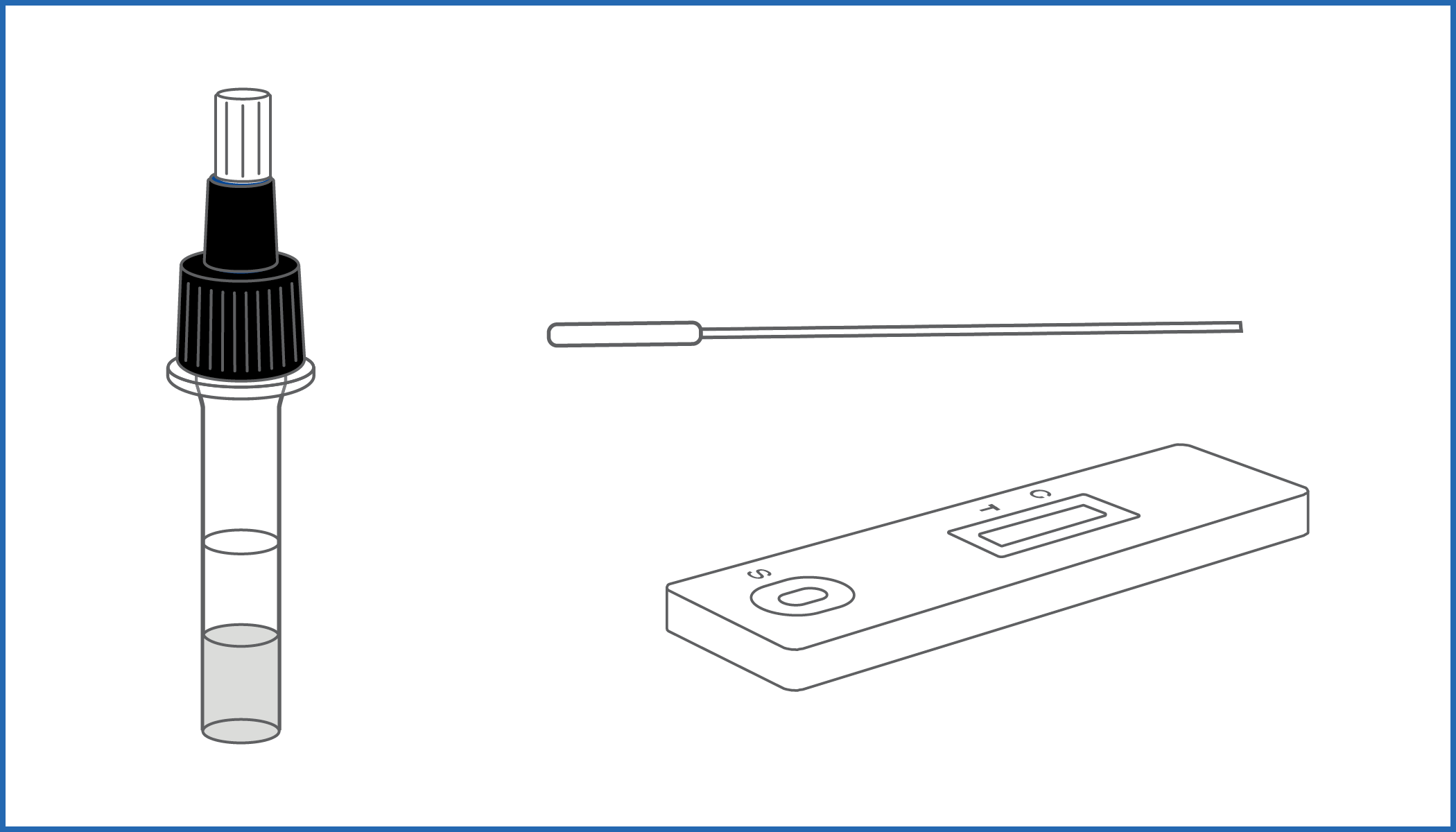
Rapid self-test for the qualitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid protein antigens in human nasal specimens.
Inserted in the rapid self-test swabs list for the Emilia Romagna region, Italy.

Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has been recognized as the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic.
read moreAs with other respiratory diseases, SARS-CoV-2 can cause an asymptomatic infection, causing mild symptoms such as cold, sore throat, cough and fever, loss of taste and/or sense of smell, or more severe symptoms such as pneumonia and respiratory distress with a fatal outcome. The incubation period of SARS-CoV-2 varies from 1 to 14 days.
COVID-19 ANTIGEN SELF-TEST is dedicated for anyone who wants to verify a possible SARS-CoV-2 ongoing infection.
read moreAntigenic tests for COVID-19 allow to carry out a qualitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 in nasal samples and are intended as rapid diagnostic devices to be carried out for home use. It is recommended to use COVID-19 ANTIGEN SELF-TEST during the time frame relating to possible exposure to the virus.
COVID-19 ANTIGEN SELF-TEST is an immunochromatographic assay for the qualitative detection of Nucleocapsid antigens in nasal specimens.
| Specificity symptomatic subjects | 99.5% |
| Specificity asymptomatic subjects | 99% |
| Sensitivity symptomatic subjects | 97.2% |
| Sensitivity asymptomatic subjects | 97.8% |
| Accuracy symptomatic subjects | 98.6% |
| Accuracy asymptomatic subjects | 98.4% |



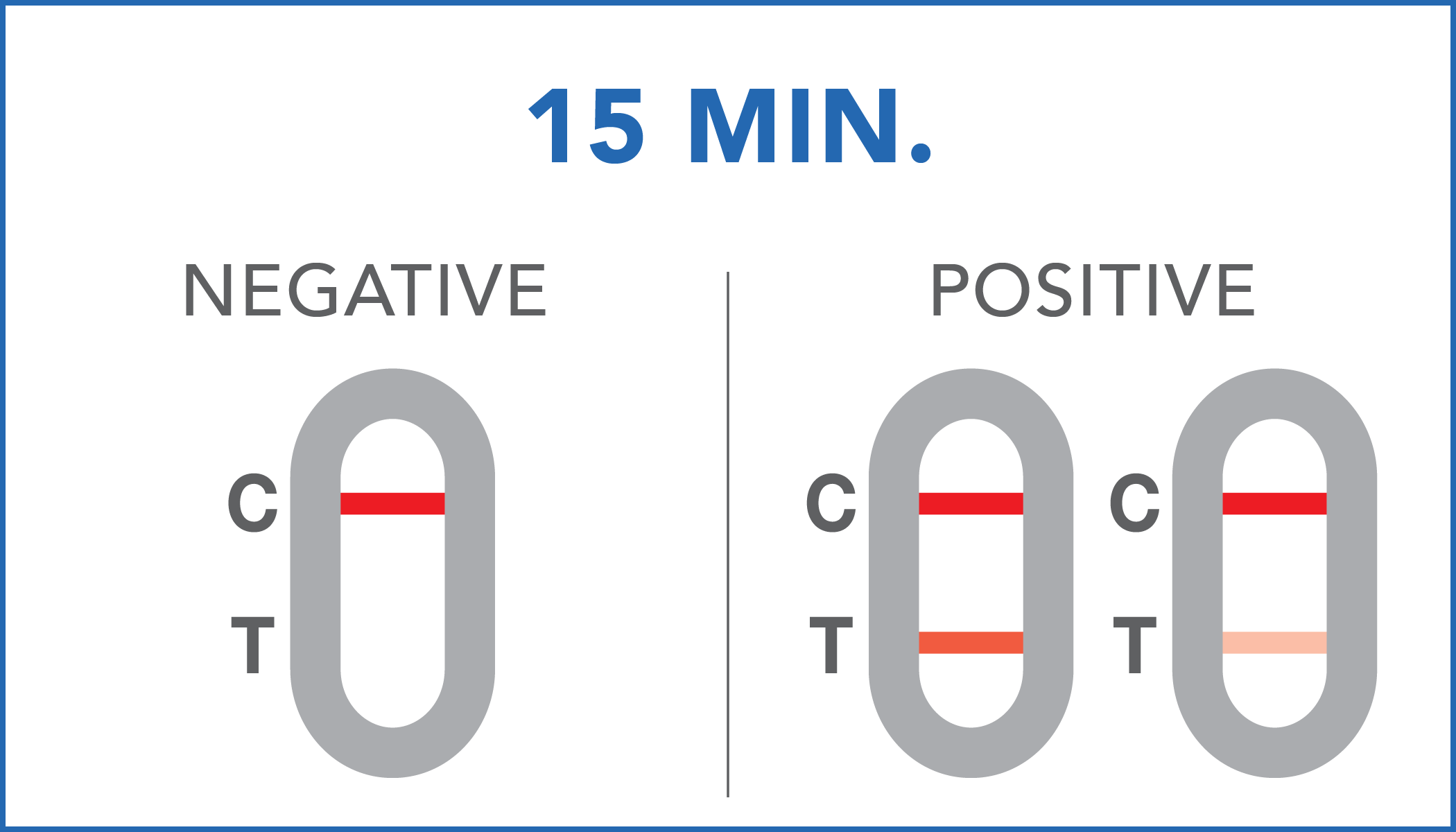
| Negative | SARS-CoV-2 antigens levels are not present in the sample or they are present in very low concentrations, which are not detectable by the device. |
| Positive | SARS-CoV-2 antigens have been detected by the diagnostic system. It is suggested to contact a specialist or the local health department for further information. |
1. Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (Trial Version 7). National Health Commission & National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2020.
2. WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020 (https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020)
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Interim Guidelines for Collecting, Handling, and Testing Clinical Specimens for COVID-19 (https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/guidelines-clinicalspecimens.html)
4. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Options for the use of rapid antigen tests for COVID-19 in the EU/EEA - first update. 2021. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/optionsuse-rapid-antigentests-covid-19-eueea-first-update
5. WHO, Advice on the use of point-of-care immunodiagnostic tests for COVID-19
https://www.who.int/ news-room/commentaries/detail/advice-on-the-use-ofpoint-of-care-immunodiagnostic-tests-for-covid-19
6. Council of the European Union, Council Recommendation on a common framework for the use and validation of rapid antigen tests and the mutual recognition of COVID-19 test results in the E, 20 January 2021
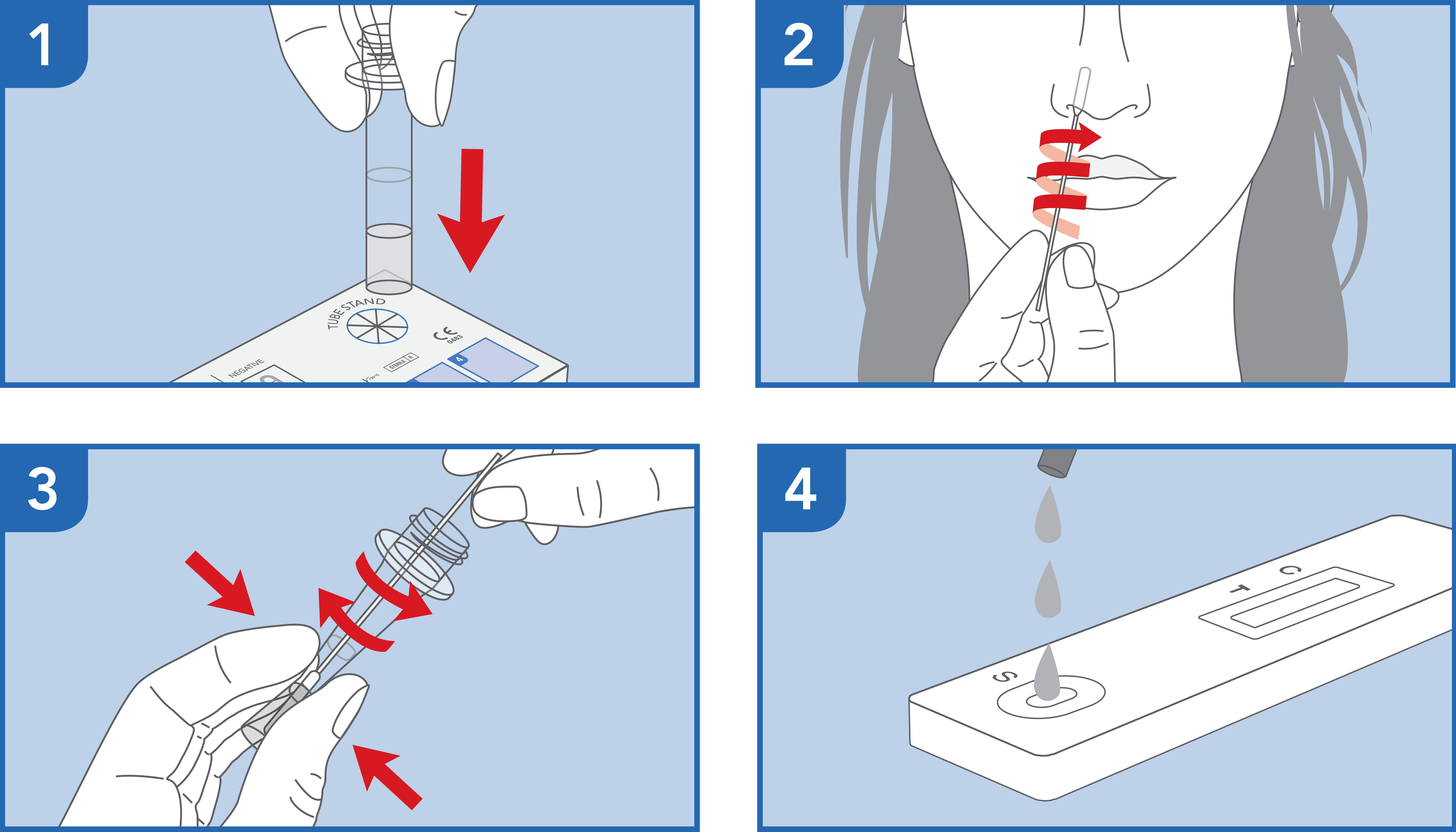
The test has been carried out correctly when the instructions for use are followed. It includes the reading time and the interpretation of the results shown at the "RESULTS INTERPRETATION" section of the instructions for use.
It is advisable to perform the test in the presence of symptoms attributable to COVID-19, or if it is suspected that you have come into contact with positive subjects in the last 5 days.
The color intensity of the control and test bands may vary depending on the concentration of antigens present in the sample. Therefore, any color hue in the test region (T) should be considered as positive.
Check product availability with the local representative in your country