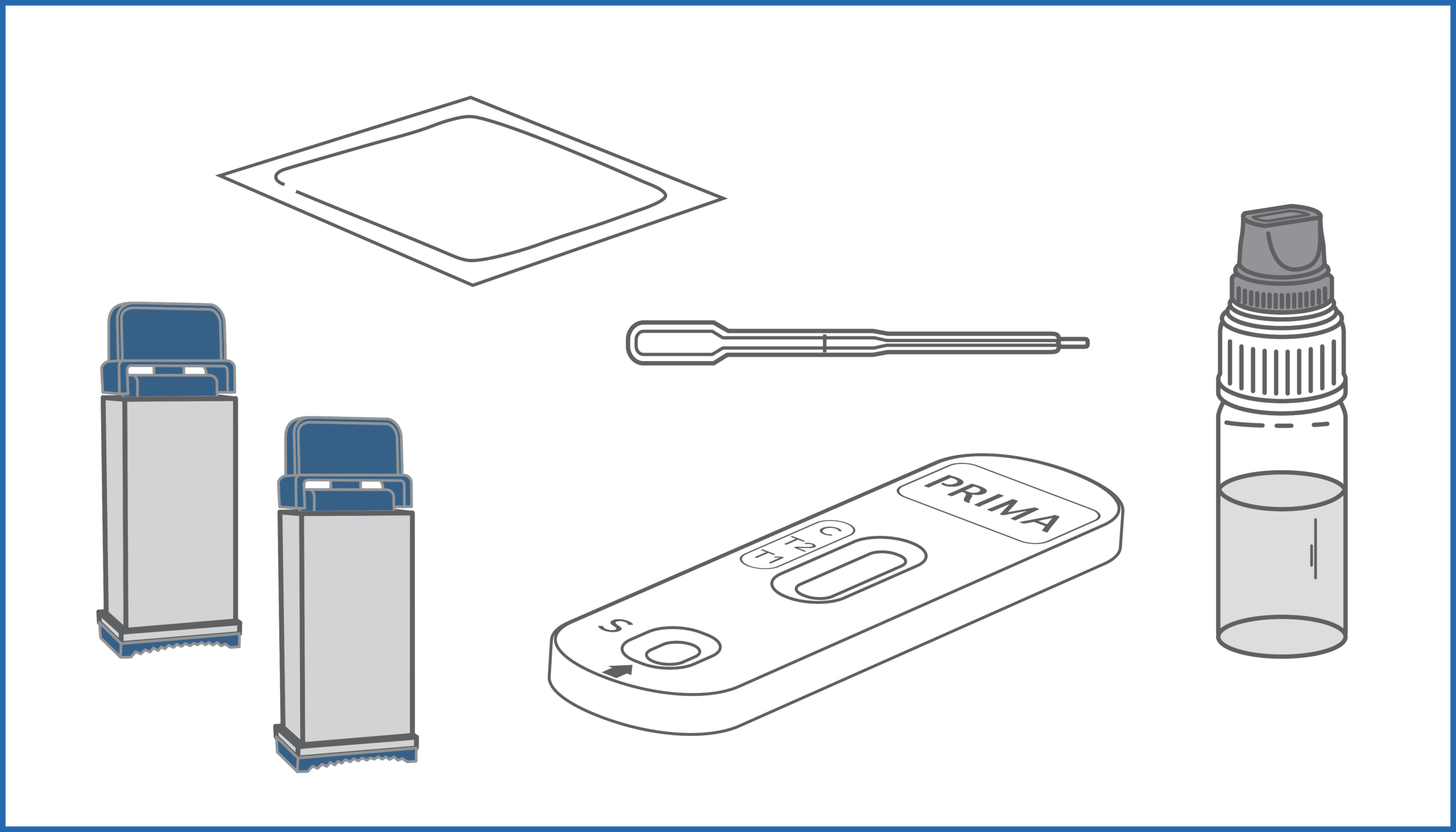
Rapid immunochromatographic manual self-test for the qualitative detection of anti-Deamidated Gliadin Peptide IgG and anti-tissue Transglutaminase IgA in human capillary blood sample for the screening of celiac disease

Celiac disease is a chronic autoimmune intestinal disease caused by the ingestion of gluten, which, in genetically predisposed individuals, results in a state of chronic inflammation of the small intestine. It can occur at any age, and a prevalence of 1.5% among the world population, with a higher incidence in the female sex.
Recent studies have shown that celiac sufferers produce specific antibodies that are detectable in the blood. Among them, IgG anti-deamidated gliadin peptides (anti-DGP) and anti-tissue transglutaminase (tTG) antibodies show a high correlation with celiac disease, thus allowing high accuracy in screening for the disease.
In people with celiac disease, the gluten exposure – a protein complex typical of certain cereals – leads to a progressive reduction of the villi that line the small intestine, until they disappear completely. This interferes with the absorption of nutrients, since the intestinal villi are responsible for this, which in the long term leads to weight loss and growth retardation.
CELIAC DISEASE SCREENING TEST is indicated both for those with the classic symptoms relatable to celiac disease and for those individuals who experience vitamin deficiencies. Since celiac disease is a heritable condition, the test is also recommended for those who have family members with celiac disease or who belong to specific risk groups (patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, Down syndrome, osteoporosis, iron deficiency anemia).
read moreCommon symptoms include chronic diarrhea, abdominal pain and bloating, constipation, and weight loss. Some individuals have less frequent symptoms such as headache, lethargy, and joint pain. Any vitamin deficiencies (e.g. iron, vitamin B, or folate), could be an indication of improper intake of necessary nutrients, caused precisely by celiac disease.
In addition, the risk of positivity has been found to increase up to 20% for first-degree relatives, even if asymptomatic.
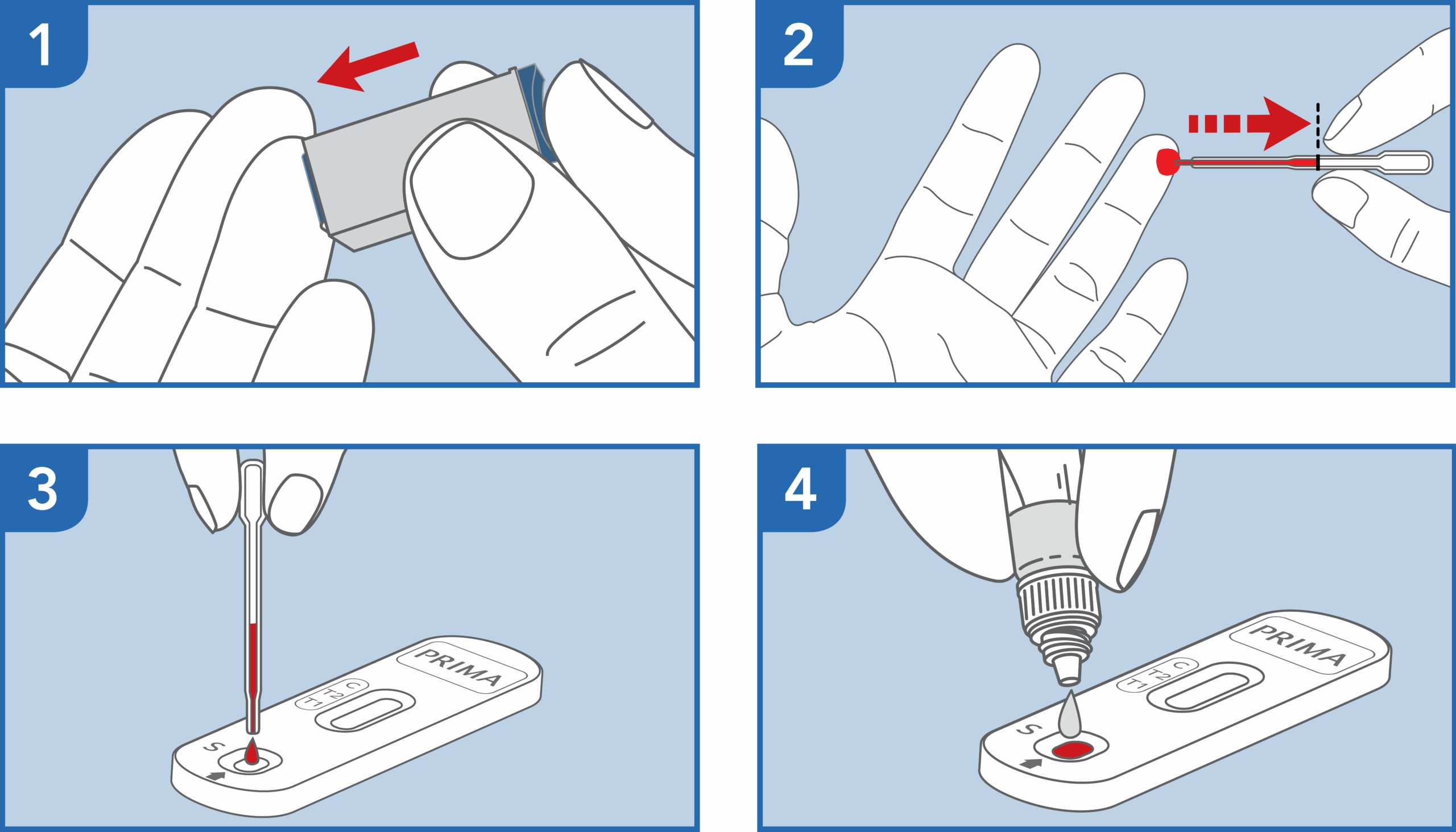
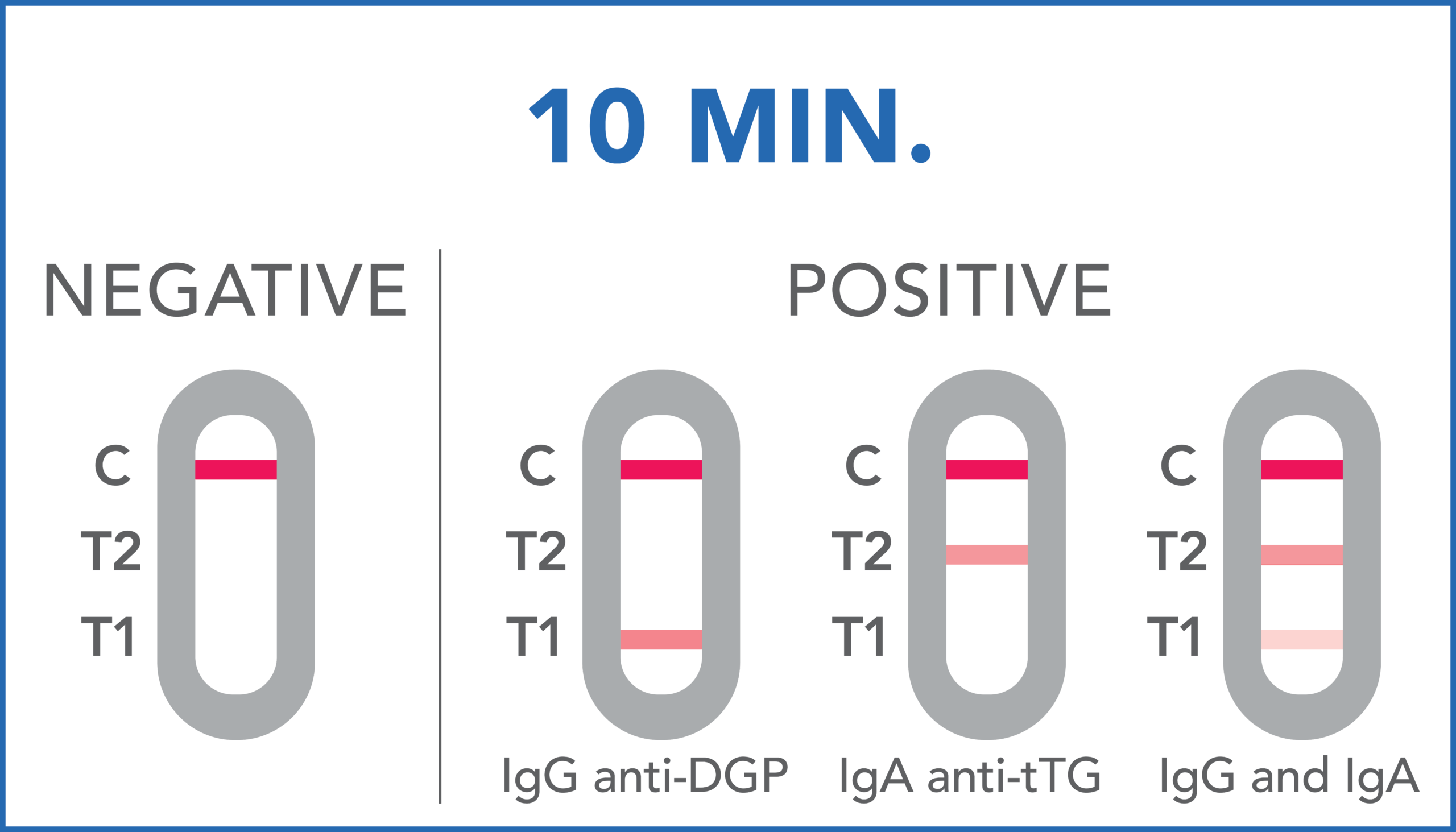
CELIAC DISEASE SCREENING TEST is a lateral flow immunochromatographic device for the detection of IgA anti-tTG and IgG anti-DGP antibodies in whole blood. During testing, the IgG anti-DGP and IgA anti-tTG antibodies, if present in capillary blood sample, react with DGP and anti-human IgA antibodies coated with gold nanoparticles present in the gold pad of the test. The mixture chromatographically migrates upward in the strip membrane by capillary action thanks to diluent addition to the strip, and interact with the test lines regions, in which an anti-DGP antibody (T1) and anti-tTG (T2) are sprayed, resulting in the appearance of colored lines.
| Specificity anti-DGP | 90.10% |
| Sensitivity anti-DGP | 84.30% |
| Accuracy anti-DGP | 86.94% |
| Specificity anti-tTG | 98.02% |
| Sensitivity anti-tTG | 98.31% |
| Accuracy anti-tTG | 98.17% |



Negative: no anti-DGP IgG nor IgA anti-tTG antibodies are present in the blood or that their level is below the limit detectable by the test.
Positive: anti-DGP and/or anti-tTG antibodies have been detected in the sample, thus a possible celiac disease. It is necessary to check with a specialist.
1. Lindfors, K., Ciacci, C., Kurppa, K. et al. Coeliac disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 5, 3 (2019).
2. Al-Toma et al. European Society for the Study of Coeliac Disease (ESsCD) guideline for coeliac disease and other gluten-related disorders. United European Gastroenterol J. 2019 Jun;7(5):583-613.
3. King, et al. 2020. Incidence of Celiac Disease Is Increasing Over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. The American Journal of Gastroenterology 115 (4): 507–25.
4. Parrinello G., Da Re M., Grizzo F., Camelliti S., Cozzi M., Marinoni F., Villalta D. Diagnostic accuracy of a novel point-of-care test for simultaneous detection of anti-transglutaminase IgA and anti-deamidated gliadin IgG antibodies. J Clin Lab Anal. 2024.
The test has been carried out correctly when the instructions for use are followed. It includes the reading time and the interpretation of the results shown at the "RESULTS INTERPRETATION" section of the instructions for use.
A colored line will appear at the control region (C) on the test device, showing that the test performed correctly. The absence of the colored line suggests to repeat the test with a new device and a new sample.
The color and intensity of the lines do not affect the interpretation of the result. The test is to be considered positive regardless of the color intensity of the test lines (T1 and T2).
Check product availability with the local representative in your country